New Jersey Council for the Social Studies
Engaging High School Students in Global Civic Education Lessons in U.S. History
The relationship between the individual and the state is present in every country, society, and civilization. Relevant questions about individual liberty, civic engagement, government authority, equality and justice, and protection are important for every demographic group in the population. In your teaching of World History, consider the examples and questions provided below that should be familiar to students in the history of the United States with application to the experiences of others around the world.
These civic activities are designed to present civics in a global context as civic education happens in every country. The design is flexible regarding using one of the activities, allowing students to explore multiple activities in groups, and as a lesson for a substitute teacher. The lessons are free, although a donation to the New Jersey Council for the Social Studies is greatly appreciated. www.njcss.org
Era 12 Postwar United States: Cold War (1945 to early 1970s)
The middle of the 20th century marks the zenith of American power in the world. Following World War 2, international organizations were established to maintain a stable world order. The United States developed alliances to counter the threat of communism and authoritarian governments. The cost of the arms race and role as ‘global policeman’ was costly for the government of the United States and as a result its defense of democracy and human rights faced criticisms from its elected representatives and people.
Activity #1: Bay of Pigs Invasion and Crimean Peninsula Invasion
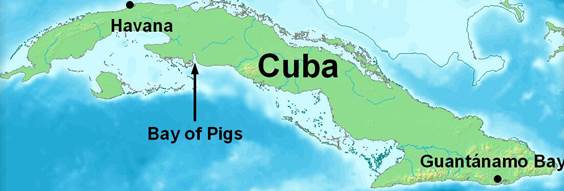
In 1959, Fidel Castro came to power in an armed revolt that overthrew Cuban dictator Fulgencio Batista. The U.S. government distrusted Castro and was wary of his relationship with Nikita Khrushchev, the leader of the Soviet Union. President Eisenhower approved the training of a small army for an assault landing and guerilla warfare. The success of the plan depended on the Cuban population joining the invaders.
On April 17, 1961 the Cuban-exile invasion force landed at beaches along the Bay of Pigs and immediately came under heavy fire. Within 24 hours, about 1,200 members of the invasion force surrendered, and more than 100 were killed. The Bay of Pigs invasion was a disaster for the United States and President Kennedy.

In 2014, Russia invaded the Crimean Peninsula in Ukraine. Russia annexed Ukraine but the international community did not support or recognize the actions of Russia. Since 2014, Russia has tightened its grip on Crimea. It has transformed the occupied Ukrainian peninsula into a military base, utilizing it for the full-scale invasion of Ukraine in 2022. Crimea currently serves as an important logistical hub for the Russian military, acting as an airbase and naval base while playing a key role in the resupply of the Russian army in Ukraine.
Russia’s Invasion of Crimea in 2014
Questions:
- Did the United States have a right to overthrow an unelected ruler in Cuba who supported the Soviet Union?
- To what extent does geography, national security, or economic stability justify actions of large sovereign states interfering in domestic affairs in smaller states?
- Why did the international community fail to challenge Russia’s invasion of Ukraine in 2014?
- Why does Russia want territory in Crimea and Ukraine?
- How can the international community best address the situation in Ukraine?
- If the international community accepts Russia’s illegal annexation of territory in a neighboring state, does this allow or encourage other countries to annex territories. (i.e. China, United States, etc.)
Activity #2: Human Rights Issues and Asylum Policies
As Americans enjoyed their new prosperity and role as the leader of the free world, there were voices for equality from women, African Americans, and people of color. The US also embraced global responsibilities and the threat posed by the expansion of communism.
Most Americans believe that freedom is a fundamental human right. In the post-World War 2 era, The United States found that the cost of defending democracy and human rights was expensive and difficult. In the first quarter of the 21st century, the United States experienced a state sponsored terririst attack on New York City and Washington D.C., threats of international terrorism, a divided Congress, unprecedented national debt, and conflicts in the Middle East. In 2025, there were 59 violent conflicts in the world. The interests of Russia and China are in conflict with the interests of the United States to defend democratic values and institutions and human rights.
The United States has not ratified the following international agreements on human rights:
- International Criminal Court
- Convention on the Elimination of All Forms of Discrimination against Women (CEDAW)
- Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC)
- Convention for the Protection of all Persons from Enforced Disappearance
- Mine Ban Treaty
- Convention on Cluster Munitions
- Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (CRPD)
- Optional Protocol to the Convention against Torture
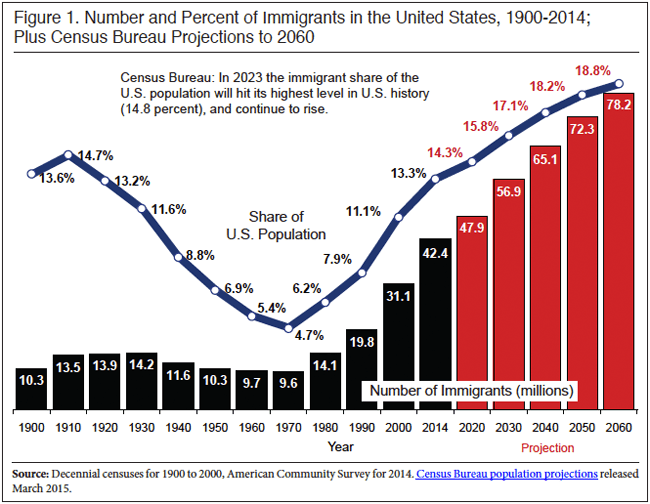
Before 1950, the United States had no stated policy on asylum. However, between 1933-1945, about 200,000 refugees fleeing the violence of war, immigrated to the United States. The American people were opposed to changing the National Origins Quota System enacted in 1924.
The 1952 McCarran-Walter Act was passed over President Truman’s veto. It continues to serve as the basis of our immigration laws and policies.
“The bill would continue, practically without change, the national origins quota system, which was enacted, into law in 1924, and put into effect in 1929. This quota system—always based upon assumptions at variance with our American ideals—is long since out of date and more than ever unrealistic in the face of present world conditions.
This system hinders us in dealing with current immigration problems, and is a constant handicap in the conduct of our foreign relations.”
In 1965 Immigration and Nationality Act (Hart-Celler Act) eliminated the quota system that was part of the McCarran-Walter Act. The Act opened immigration to people of different racial and ethnic populations, especially Asians and Africans, it continued the quotas for Mexicans and Hispanic populations and favored visas for skilled workers over agricultural or domestic workers.
According to the UN refugee agency, a record-breaking 3.6 million new individual asylum applications were registered worldwide in 2023 with most new asylum claims made by nationals of Afghanistan, Colombia, Sudan, Syria, and Venezuela. At the close of 2023, 6.9 million asylum seekers worldwide still had pending asylum claims.
In the United States in 2023, nearly half of all asylum approvals were for people fleeing Afghanistan, China, El Salvador, and Venezuela from violence, poverty, and political upheaval.
Questions:
- Why has the United States refused to support international laws on human rights and crimes against humanity since World War 2?
- Is there evidence that the United States violates the human rights of some of its own citizens?
- Why have the American people reflected a restrictive immigration policy over time, even for refugees facing death or abuse in their home country?
- Who should be granted asylum in the United States?
History of Child Labor in the United States
Brown University’s Slavery and Justice Report
The National Council of La Raza
The Immigration and Nationality Act of 1952(McCarran-Walter Act)
The 1965 Immigration Act: Opening the Nation to Immigrants of Color(Gilder Lehrman Institute of American History)
How Should Americans Remember the 1965 Immigration and Nationality Act?(Organization of American Historians)
How the U.S. Asylum Process Works(Council on Foreign Relations)
Activity #3: The Deportation of People for Their Political Views
In the years after World War 2, especially after Churchill’s Iron Curtain Speech in 1946, the United States feared a global domination of communism. This belief gained popularity after China became communist in 1949. The current administration of President Trump is identifying the Democratic party with Marxist-Leninist ideology or progressive ideas for universal health care, helping students to repay college loans, raising the minimum wage, labor unions, and deporting immigrants with legal visas and some who are not documented.
This has a ‘chilling effect’ on people, especially educators and college professors who teach about communism and Marxist socialism. It is important to understand the historical perspective over time regarding how the government of the United States has responded to situations which have called for a change in our government through elections and the violent overthrow of our Constitution and democratic institutions.
Historical Context
Congress has the power to protect the Government of the United States from armed rebellion. The Insurrection Act of 1807 combined a series of statues to protect the United States from angry citizens following the Embargo Act. The issue for debate is when does the protection of free speech regarding criticism of government policies and organizing plans to change government policies or elected leaders become a matter permitting the government to use military force to protect itself.
The Posse Comitatus Act forbids the U.S. military, including federal armed forces and National Guard from enforcing civil law. The reason for this is to protect the First Amendment rights of citizens to express their beliefs. The Stafford Act (1988) permits the use of the military in times of natural disasters or public health epidemics.
Section 252 the Insurrection Act allows the president to deploy troops without a request from the state and provides the authority to send in troops against the state’s wishes to enforce the laws of the United States or to suppress rebellion. President Eisenhower used this power to enforce the decision of the U.S. Supreme Court to desegregate the public schools in Little Rock, AK. In 1992, the governor of California requested President George H.W. Bush to send troops to control the rioting in Los Angeles following the acquittal of four white police officers on the beating of Rodney King. Section 253 allows the president to suppress domestic violence, a conspiracy to overthrow the government, or an insurrection. John Brown’s raid in 1859 and the Civil War are examples.
The Smith Act was passed in 1940 making it a crime for any person knowingly or willfully to advocate the overthrow or destruction of the Government of the United States by force or violence. This Act led to the arrest of leaders of the Communist Party who were advocating to overthrow the government of the United States by force.
In 1951, the Court ruled in a 6-2 decision that the conviction of Eugene Dennis of conspiring and organizing for the overthrow and destruction of the United States government by force and violence under provisions of the Smith Act. In 1967, the decision was overturned by the Brandenburg v. Ohio when the Supreme Court held that “mere advocacy” of violence was protected speech.
In New York, the Feinberg Law banned from the teaching of the violent overthrow of the government of the United States. Several other states adopted similar measures. When a group of teachers and parents challenged this law, the Supreme Court upheld it in Adler v. Board of Education of the City of New York, (1952) In 1967, another Supreme Court overturned the Adler decision.
Questions:
- If the Declaration of Independence states the right of people to dissent and overthrow an unjust government, should school teachers be allowed to teach this to young students?
“That whenever any Form of Government becomes destructive of these ends, it is the Right of the People to alter or to abolish it, and to institute new Government, laying its foundation on such principles and organizing its powers in such form, as to them shall seem most likely to effect their Safety and Happiness. Prudence, indeed, will dictate that Governments long established should not be changed for light and transient causes; and accordingly all experience hath shewn, that mankind are more disposed to suffer, while evils are sufferable, than to right themselves by abolishing the forms to which they are accustomed. But when a long train of abuses and usurpations, pursuing invariably the same Object evinces a design to reduce them under absolute Despotism, it is their right, it is their duty, to throw off such Government, and to provide new Guards for their future security.”
2. Why do you think the U.S. Supreme Court overturned the Dennis and Adler decisions years later? Do these reversals have a strong foundation in American law?
3. Is it possible to use the Smith Act and the Insurrection Act to bring about a change in government that would embrace a more authoritarian government and a less democratic one?
4. How can the Smith Act and Insurrection Act be abolished? Should they be abolished?
5. What is the biggest threat facing the United States in the future? (natural disaster, political violence, artificial intelligence, public health emergency, economic crisis, etc.) Will the best solutions to this threat come from the Executive, Legislative, or Judicial branch of our government?
Thomas Jefferson Signs the Insurrection Act into Law, March 3, 1807
The Insurrection Act Explained (Brennan Center for Justice)
Supreme Court Rules on Communist Teachers (Adler v. Board of Education of City of New York)
Insubordination And ‘Conduct Unbecoming’: Purging New York’s Communist Teachers at the Start of the Cold War (The Gotham Center for New York City History)
Mass Deportation: Analyzing the Trump’s Adminsitration’s Attacks on Immigrants, Democracy, and America(American Immigration Council)
Activity #4: The Return of Veterans from World War 2 in the United States and Japan
Japan officially surrendered on September 2, 1945. More than 400,000 Americans, and an estimated 65 million people worldwide, died during the war. After the surrender, the repatriation of the soldiers to their home country began. Refugees also began to return to their homes. The return of the soldiers to Japan, Soviet Union, European countries, and the United States was very different. In this activity, you will compare the return of 7 million soldiers to Japan and the United States. The United States had 16 million soldiers in uniform and 8 million of them were overseas. Operation Magic Carpet was the program to transport Japan’s soldiers to their homeland. There were also millions of Korean and Chinese civilians the Japanese used as slave labor during the war who needed to be repatriated.
Japan’s navy and merchant marine navy had been destroyed during the war. The carriers Hosho and Katsuragi, the destroyer, Yoizuki, and the passenger ship, Hikawa Maru, were able to transport some Japanese soldiers. The United States, Soviet Union, and England used their ships to bring 6.6 million Japanese soldiers back to Japan. The Japanese government designated 18 ports to receive their soldiers. The U.S. role was completed by the end of 1947. The Soviet Union’s role continued through 1957. The port of Maizuru was the largest port.

The Japanese soldiers were sprayed with the chemical DDT (dichloro-diphenyl-trichloro-ethane) to kill fleas and lice. At the time, DDT was considered a ‘safe’ chemical but in 1972 it was known to be harmful. Welcome towers were erected where citizens welcomed the retuning soldiers.
The United States also used Nisei interpreters during the years after the surrender of Japan (1945-1952) to prosecute Japan’s military leaders for war crimes, detect subversive activities and help with the drafting of Japan’s new constitution.
Most cities and homes in Japan were destroyed as a result of the war and the destruction of the two atomic bombs. Almost every family experienced the death of a loved one and they did not have a proper burial or the return of their personal belongings (sword, identification, notebooks, clothing, etc.) The new government in Japan changed the family structure which encouraged marriage and children.
The Return of Soldiers to the United States
The return of veterans to the United States began in 1944, shortly after D-Day. The government instituted a point system based on battles for the return home after the war ended and the GI Bill, which provided for education and vocational training, credit towards loans, one year of unemployment compensation, and counseling. The purpose of the GI Bill was to avoid the high unemployment and inflation that followed World War I.

“Veterans Prepare for Your Future thru Educational Training, Consult Your Nearest Office of the Veterans Administration,” n.d. Courtesy of NARA, 44-PA-2262, NAID
The repatriation of American soldiers was very successful and the income taxes from their wages paid back the cost of the GI Bill within the first few years. Veterans also purchased new homes which also increased the GDP. Similar benefits were provided to American soldiers who served in Korea and Vietnam. New car sales also quadrupled in the first ten years following World War 2 and by 1960 about 75 percent of American households owned a car.
Questions:
- Why did the United States spend millions of dollars to repatriate Japanese soldiers to Japan after the surrender and why did our government pay for the inoculations and transportation of Korean and Chinese from Taiwan?
- What would the post-war years in Japan be like without the financial and technical assistance of the United States and the Allied Powers?
- As a member of Congress, would you have supported the GI Bill in 1944 knowing that the national debt of the United States was 120% above our GDP?

- Was it fair to provide ships to transport Japanese soldiers home before all of the American soldiers were repatriated?
- Should the United States have done more (or less) to repatriate the soldiers from Japan?
Maizuru Repatriation Memorial Museum
The Afterlife of Families in Japan (Texas A&M University, Corpus Christi)
The American Soldier in World War 2
Veterans Return Home From World War 2 (U.S. Army Documentary)
Serviceman’s Readjustment Act, 1944 (National Archives)



