New Jersey Council for the Social Studies
Engaging High School Students in Global Civic Education Lessons in U.S. History
The relationship between the individual and the state is present in every country, society, and civilization. Relevant questions about individual liberty, civic engagement, government authority, equality and justice, and protection are important for every demographic group in the population. In your teaching of World History, consider the examples and questions provided below that should be familiar to students in the history of the United States with application to the experiences of others around the world.
These civic activities are designed to present civics in a global context as civic education happens in every country. The design is flexible regarding using one of the activities, allowing students to explore multiple activities in groups, and as a lesson for a substitute teacher. The lessons are free, although a donation to the New Jersey Council for the Social Studies is greatly appreciated. www.njcss.org
Era 11 The Great Depression and World War II (1929–1945)
| * | |||||
| * | |||||
The beginning of the 20th century marks the foundation of the transformation of the United States into a world power by the middle of the century. In this era industrialization, urbanization, and rapid immigration changed America from an agrarian to an urban society as people lived and worked in cities. The development of the new technologies of electricity, transportation, and communication challenged our long-held traditional policies of limited government, neutrality, and laissez-faire capitalism. The lesson of the Great Depression was that capitalism and free markets did not enable everyone to attain the American Dream. As a result, Americans looked to their government for help with the problems of unemployment, poverty, old age. Housing, and the supply of food.
Activity #1: The New Deal vs. a Five-Year Plan?
During the Great Depression, the unemployment rate was 24.9% in the United States (about 13 million people). Without income, there was very limited private consumption. President Roosevelt identified the South as the number one “problem region” of the U.S. for poverty and economic distress. In 1933, President Roosevelt signed the Tennessee Valley Authority Act, a federally funded program to protect the environment from floods, encourage economic development, and produce electric power.
In 1934, Shareholders of the Alabama Power Company sued to prevent the TVA from acquiring over half of the company’s property and equipment. The sale would allow the government agency to allocate electric power to consumers. The shareholders argued that Congress exceeded its authority.
The U.S. Supreme Court in Ashwander v. Tennessee Valley Authority, held that Congress did not abuse its power. Justice Hughes argued that the Wilson Dam, the location where the TVA was in the business of generating electricity, had been built originally in the interest of national defense because it produced materials involved in the production of munitions. The government could sell excess electricity to consumers without violating the Constitution. The majority concluded that Congress had the authority to construct the Wilson Dam. The majority also found that the disposal of the electric energy generated was lawful.
This Supreme Court decision is also known for the reasoning of Justice Louis Brandeis regarding conflicts when one branch exceeds its power and infringes on another branch. Justice Brandeis adopted the criteria which has become known as the ‘avoidance doctrine.’ “One branch of the government cannot encroach upon the domain of another, without danger. The safety of our institutions depends in no small degree on a strict observance of this salutary rule.”
The legacy of the Tennessee Valley Authority brought electricity to the southeastern United States increasing the productivity of farming and transforming this region from poverty to sustainable economic development. Before the Tennessee Valley Authority, electric power was generated by private companies. (e.g. Westinghouse, Edison Electric Illuminating Company, Public Service Corporation, etc.) Private companies are concerned with making a profit instead of investing in public areas such as street lights or rural areas. The first buildings to have electricity around 1880 were often hotels and commercial buildings. Wabash, IN, Appleton, WI, Cleveland, OH, and lower Manhattan were some of the first towns and cities to have electric power. Some members in Congress, namely Senator George Norris, favored public utility companies as the most efficient way to bring this new invention to everyone in the United States.
The Soviet Union’s Five-Year Plan: The Zaporizhzhia Nuclear Power Station in Ukraine

Since the Russian Revolution of 1917, Lenin prioritized the electrification of the Soviet Union as essential for economic and industrial development. Each of the 12 Five Year Plans included the expansion of power through the construction of dams, fossil fuels, natural gas, and since 1975, nuclear energy. The Soviet state planning committee, Gosplan, developed these plans with clearly stated production goals.
One of the problems with the energy plan of the Soviet Union is the transmission of electricity from the generating plant to other regions of the country. Russia depends on a unified power system and the complexity of its geography and use of different energy sources (fossil fuels, hydropower, natural gas, and nuclear) makes it difficult to transfer power from one source to another efficiently. The heaviest demand for electricity is in the western or European side of the country. However, as electricity became accessible to rural areas, agricultural production became dependent on electricity. The largest nuclear power plant in Europe is on the Dnieper River in Ukraine. It was constructed in 1985.
The Soviet Union could benefit from the computer software used in the United States, but the Five-Year Plan model is dependent on Soviet Union computers and boilers. Some of the Five-Year Plans were completed ahead of schedule, some did not meet their goals, and they also included social changes such as closing houses of worship, providing child care, and using large collective farms. The goals of most of the plans were to transform the Soviet Union into a major industrial and economic power.
The Debate Between Private and Public Electric Companies
The Soviet Electric Power Industry
Questions:
- How is a market economy different from a command economy? What are the advantages and disadvantages of both models?
- Why did the United States and Soviet Union experience challenges or problems with electrifying their countries?
- Is a monopoly or market competition the most efficient economic model for providing utilities to the people in a country? (water, electric, phone, education, etc.)
- Is a market or command economy the most efficient model to address the expected problems from climate change in the next 25 years?
- Which economic model (market, command, or mixed) is the most efficient one to increase worker productivity?
Activity #2: Two Perspectives on World War II: DR’s Four Freedoms Speech and Hirohito’s Decree
On January 6, 1940, about three months after Hitler’s attack on Poland, President Franklin Roosevelt gave his Four Freedoms speech as part of his State of the Union address. This was during a time when many people in America wanted to remain neutral and isolated from the European conflict which expanded in September 1939 with Germany’s blitzkrieg attack and occupation of independent Poland.
1940 was also a presidential election year. In the mid-term election of 1938, the Republican Party became the majority in the House and Senate. The Republican Party had several contenders for the nomination, notably Governor Thomas Dewey (NY) Senator Robert Taft (OH), and Wendell Wilkie, a businessman from Kansas. When the Republican Party convention was held in June in Philadelphia, Wendell Wilkie’s popularity had increased significantly, while the popularity of Thomas Dewey and Robert Taft was declining.
Excerpt from the Four Freedoms Speech
“In the future days, which we seek to make secure, we look forward to a world founded upon four essential human freedoms.
The first is freedom of speech and expression–everywhere in the world.
The second is freedom of every person to worship God in his own way–everywhere in the world.
The third is freedom from want–which, translated into world terms, means economic understandings which will secure to every nation a healthy peacetime life for its inhabitants-everywhere in the world.
The fourth is freedom from fear–which, translated into world terms, means a world-wide reduction of armaments to such a point and in such a thorough fashion that no nation will be in a position to commit an act of physical aggression against any neighbor–anywhere in the world.
That is no vision of a distant millennium. It is a definite basis for a kind of world attainable in our own time and generation. That kind of world is the very antithesis of the so-called new order of tyranny which the dictators seek to create with the crash of a bomb.
To that new order we oppose the greater conception–the moral order. A good society is able to face schemes of world domination and foreign revolutions alike without fear.
Since the beginning of our American history, we have been engaged in change — in a perpetual peaceful revolution — a revolution which goes on steadily, quietly adjusting itself to changing conditions–without the concentration camp or the quick-lime in the ditch. The world order which we seek is the cooperation of free countries, working together in a friendly, civilized society.
This nation has placed its destiny in the hands and heads and hearts of its millions of free men and women; and its faith in freedom under the guidance of God. Freedom means the supremacy of human rights everywhere. Our support goes to those who struggle to gain those rights or keep them. Our strength is our unity of purpose. To that high concept there can be no end save victory.”
Historical perspectives were important in 1941, and they are important today. The United States, including President Roosevelt, presented a perspective of Japanese superiority and a destiny to rule the world. He also called America’s citizens to accept the importance of a new moral order that included the religious concept of faith in freedom under the guidance of God. This perspective of American superiority is built on a commitment to an idea and an ideal.
American vs. Japanese Civilian Perspectives
A Life Magazine article about Emperor Hirohito in 1937 stated “To Japanese he is, in all seriousness, a divine descendent of the Sun goddess, the incarnate head of the Japanese divinity idea that makes the conquest of Asia a holy destiny for the Japanese race.” For ordinary Americans, the concept of kami in Japanese culture was not comprehendible. Instead of understanding a perspective of divinity as present everywhere, they accepted Hirohito as a son of a god or goddess or someone connected with divinity.
After the bombing at Pearl Harbor tensions between the United States and Japan escalated. Through the lens of war, the Japanese emperor’s god-like status became a more serious issue because they perceived Japan’s war objectives connected with their religious beliefs. A 1945 United States News story explains, “Shintoism has no religious content and has ethical content to the extent that it is designed to support the idea of the divine origin of the Emperor.” A 1945 article in Life Magazine stated, “The Emperor of Japan is neither a man nor a ruler. Nor is he simply a god living in Tokyo. He is a spiritual institution in which center the energy, the loyalty and even the morality of the Japanese.” He is supreme in all temporal matters of state as well as in all spiritual matters, and he is the foundation of Japanese social and civil morality.
American and Japanese civilians had very opposite reactions following the events of December 7, 1941. For Americans, Pearl Harbor represented “A Day Which Will Live in Infamy.” For citizens of Japan, Pearl Harbor represented the success of a justified military retaliation. The American and Japanese governments both utilized nationalism to their advantage, and implemented various forms of propaganda as tools for shaping their civilians’ perspectives.
Excerpt from Japan’s Announcement Following the Attack on Pearl Harbor
“What an uproar! Japan’s Imperial Forces got things off to a quick start with one splendid strike then another in historic surprise attacks on Pearl Harbor, where the bravado of the US Asia fleet met with sudden defeat, and off the Malaya Coast, where the main forces of the British Asia fleet were utterly annihilated. Word has it that Roosevelt and Churchill were shaken up and went pale upon hearing of the defeats. In a third strike, Hong Kong Island, England’s strategic base for its 100-year exploitation of East Asia, fell into ruin in only a matter of ten days. During this time, Churchill was sent reeling, cutting off contact with others and showing up in Washington.
What these two headstrong countries are striving for will only lead them on a downhill path to military defeat. Our barbaric enemies are already cowering in fear in the Pacific, and the fall of Manila shall mark the day of the Philippines’ subjugation and reversion back to Greater East Asia. The enemy power of Singapore, which was—alas—boasting of its impenetrable stronghold before the Imperial Forces penetrated the jungle area of the Malay Peninsula and advanced southward like a raging tide, shall also vanish into nothingness in the midst of this glorious chapter in history.
The military gains of the glorious Imperial Forces are truly great, and the army, navy, and air force should be given our heartfelt gratitude. We should also honor our courageous men who are ready to lay down their lives when charging enemy lines, as well as those who went out to conquer but never returned.”
Emperor Hirohito’s Decree
On January 1, 1946, four months after the surrender on September 2, 1945, Emperor Hirohito made the following statement in Japan’s newspapers.
“I stand by my people. I am ever ready to share in their joys and sorrows. The ties between me and my people have always been formed by mutual trust and affection. They do not depend upon mere legends or myths. Nor are they predicated on the false conception that the Emperor is divine, and that the Japanese are superior to other races and destined to rule the world.
FDR Annual Message to Congress, January 6, 1940
Japanese vs. American Perspectives on Pearl Harbor
Japan’s Announcement Following Pearl Harbor, December 8, 1941
President Roosevelt’s Speech Following Pearl Harbor (video:4:48)
Eleanor Roosevelt’s Radio Address on the Evening of Pearl Harbor (transcript)
Eleanor Roosevelt’s Radio Address on the Evening of Pearl Harbor (audio, 2:57)
Questions:
- How was the rise of dictators after World War 1 an existential threat? How did ordinary American citizens understand the conflict in Europe and Asia before and after the attack on Poland and the attack on Pearl Harbor?
- If you were the President of the United States in 1940, would you deliver the Four Freedoms speech or one that is similar in content and context?
- Do you accept President Roosevelt’s statement following Pearl Harbor that before the attack the United States was at peace with Japan? (see video clip above)
- Are elected leaders elevated by people and the press or are they criticized to the extent that their decisions and motives are questioned?
- Which government delivered the best message to its citizens based on factual evidence and an understanding of the importance of the attack on Pearl Harbor?
Activity #3: Japanese Internment Camps and Soviet Union Deportation Camps
Japanese Internment Camps

Two months after the attack on Pearl Harbor, February 19, 1942, President Franklin Roosevelt signed Executive Order 9066 to relocate approximately 117,000 Japanese Americans living on the west coast. At first, the order was voluntary and Japanese Americans had time to sell their property and comply in an orderly manner.

Unfortunately, many did not comply voluntarily, and the relocation became mandatory. Thousands of people lost their homes and businesses due to “failure to pay taxes.” The relocation of Japanese Americans in the United States for safety and security reasons was controversial during World War II and for the decades that followed. The internment camps provided educational and recreational activities, adequate heat, and a process to hear complaints and address concerns.

There were 12 camps located all over the United States, with the Seabrook Farms camp in New Jersey.

President Truman rescinded the Executive Order on June 25, 1946 allowing the Japanese Americans to return to their homes. They were in relocation camps for more than four years. When they returned home, most found their belongings stolen and their homes and property sold. They also faced prejudice and discrimination for years, even though Japanese Americans were combat soldiers during the war.
In 1988, President Ronald Reagan signed the Civil Liberties Act. The remaining survivors of the relocation camps were sent formal letters of apology and were awarded $20,000 in restitutions from the United States government.
Soviet Union Deportation Camps During World War II
On February 23, 1944, the Chechens were exiled from their ancestral lands and deported to Siberia and the northern regions of Kazakhstan. The entirety of the Chechen nation was accused of collaborating with the Fascists, even though there is no evidence to support this. The German advance into the Soviet Union never came close to Chechnya. The Chechen deportation of almost 400,000 men, women, and children is the largest Soviet deportation and occurred in a matter of days. Many Chechens had in fact fought on the front lines of the Soviet war against the German aggressor.
On September 1, 1941 the mass evacuation was announced for the approximately 440,000 Volga Germans. Ten days later they began their forced deportation to Kazakhstan and Siberia. Many were forced to work in ‘labor camps’ such as Kolyma. The Volga Germans were then stripped of their citizenship and did not regain their civil rights until after Stalin’s death. Most estimates indicate that close to 40 percent of the affected population perished.
In 1944, Joseph Stalin ordered the deportation of the entire Crimean Tatar community (roughly 200,000), falsely accusing them of collaborating with the Nazis. Reports suggest that nearly half of the deported died during the ordeal. Ukraine, Latvia, Lithuania, and Canada have all formally recognized Stalin’s brutal deportation as a crime of genocide. During this same period, the Soviet Union adopted a policy of “Russification” for the peninsula. Crimea was “Russified” and any study of the Tatar’s native language was banned, ancient Tatar names were erased, Tatar books were burned, and their mosques were destroyed. Nikita Khrushchev transferred Crimea from Soviet Russia to Soviet Ukraine.
Behind Barbed Wire: Japanese American Camps
Japanese American Internment Camps
Soviet Union Deportation of Volga Germans
Soviet Union Deportation of Chechnyas
Soviet Union Deportation of Crimean Tatars
Questions:
- Is it possible for a government to correct something it did that was morally or legally wrong?
- Do governments need to justify the actions they take during a time of war or a national crisis?
- Are there significant differences in the actions of the United States and the Soviet Union in the relocation or deportation of innocent people, many who were citizens?
- Do ordinary people have any rights during a war or crisis (i.e. Ukraine, Gaza, Sudan, Congo, Rwanda, etc.)?
- How and who determines if and when a government exceeds its authority?
Activity #4: Weapons of Mass Destruction

In World War II, the Japanese were fighting for the Emperor who convinced them that it was better to die than surrender. Women and children had been taught how to kill with basic weapons. kamikaze pilots crashed their planes into American ships. A land invasion would be costly with estimates of more than one million American lives lost.
After a successful test of a nuclear bomb at Los Alamos, New Mexico on July 16, 1945, the United States, China, and the United Kingdom issued the Potsdam Declaration on July 26 demanding the unconditional surrender of the Japanese government, warning of “prompt and utter destruction.” On the morning of August 6, 1945, the first atomic bomb was dropped on Hiroshima. The result was approximately 80,000 deaths in just the first few minutes. Thousands died later from radiation sickness. On August 9, 1945, a second atomic bomb was dropped on Nagasaki. The result was 39,000 men, women and children were killed and 25,000 more were injured. Both cities were leveled and Japan surrendered to the United States.
After the news of the atomic bombs that were dropped on Hiroshima on August 6, 1945 and on Nagasaki on August 9, 1945, Lieutenant General Leslie R Groves, director of the `Manhattan Project’ that had developed the atomic bomb, commented:
“The atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki ended World War II. There can be no doubt of that. While they brought death and destruction on a horrifying scale, they averted even greater losses – American, English, and Japanese”.
This justification that the use of the bomb saved lives, even though it killed innocent civilians, has haunted the world into our present time. It was a view that generated controversy then and after as to the justification or otherwise of the use of such weapons on largely defenseless civilian targets, at such Mutual Assured Destruction (MAD) that has haunted the world into our present times.
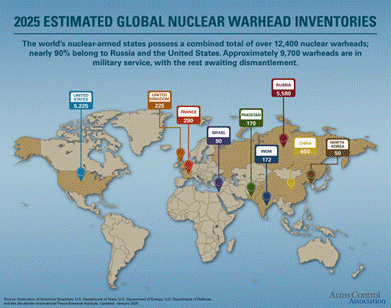
Following World War 2, there was an arms race between the Soviet Union and the United States. Although there were threats of war and conflicts in Korea, Southeast Asia, the Congo and other places, this period was called the Cold War. Other countries also developed nuclear weapons leading to concerns of a global conflict.
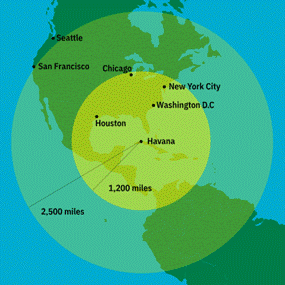
The world came close to a nuclear attack during the Cuban Missile Crisis. In 1962, nuclear weapons could be delivered by airplanes, missiles, and submarines. The Soviet Union placed nuclear warheads in Cuba and the United States had some in Turkey. These missiles could attack cities in both countries within a range of 1,200 miles. Fortunately, the Soviet Union began to withdraw its ships and missiles from Cuba and an agreement was made.
In the 1960s, the military strategy of Mutual Assured Destruction (MAD) was debated, In this strategy, two opposing forces, the Soviet Union and the United States, had enough nuclear weapons to completely destroy each other. This deterrence theory assumed that neither side would initiate a nuclear attack because the resulting retaliation would lead to their own destruction. The concept, first discussed in the 1960s during the Cold War, is based on the idea that the devastating consequences of nuclear war would outweigh any potential gains for either side.
As a result, the United Nations initiated the process to limit the production of nuclear testing and weapons. Since the first test ban treaty, several agreements have been ratified to control the proliferation of nuclear and chemical weapons. The threat from atomic, hydrogen, neutron, and cobalt nuclear weapons is a concern to every person and every country because of the fallout from dangerous levels of radiation. There are still detectable effects of radiation in our atmosphere today from the 1945 explosion. The effects of radiation from a thermonuclear weapon (Hydrogen bomb) will likely last for hundreds of years and affect every living organism and human.
Following the Attack on the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001, the world became concerned about a terrorist group having access to a smaller nuclear weapon, a dirty bomb, that might be detonated in an urban area. The effects of a dirty bomb would likely be limited to the immediate area of the explosion but the damage to property and the cleanup of radioactive elements would be significant and costly.
Nuclear Arms Race and Treaties: 1949-2021 (Council on Foreign Relations)
Timeline of the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (Arms Control Association)
Devastating Effects of Nuclear Weapons
Questions:
- Why did an arms race between the USA and the USSR begin after 1945?
- How sane was the policy of MAD?
- What factors sustained the arms race for so long?
- Is a limited nuclear war a plausible scenario or would it quickly lead to an all-out war?
- What would life on Earth be like after a nuclear war? What geographic regions might have a chance of survival?
- Should the civil defense from a nuclear war or dirty bomb explosion be best coordinated by local, state, or the federal government in the United States?
- How would the governments of Europe or the Middle East, where there are many countries within a small geographic area respond to a nuclear war or explosion from a bomb or nuclear power plant?
- What is the most likely scenario for a nuclear explosion in the 21st century?

