New Jersey Council for the Social Studies
Engaging High School Students in Global Civic Education Lessons in U.S. History
The relationship between the individual and the state is present in every country, society, and civilization. Relevant questions about individual liberty, civic engagement, government authority, equality and justice, and protection are important for every demographic group in the population. In your teaching of World History, consider the examples and questions provided below that should be familiar to students in the history of the United States with application to the experiences of others around the world.
These civic activities are designed to present civics in a global context as civic education happens in every country. The design is flexible regarding using one of the activities, allowing students to explore multiple activities in groups, and as a lesson for a substitute teacher. The lessons are free, although a donation to the New Jersey Council for the Social Studies is greatly appreciated. www.njcss.org

Era 5 The Development of the Industrial United States (1870–1900)
The development of the industrial United States is a transformational period in our history. The United States became more industrial, urban, and diverse during the last quarter of the 19th century. The use of fossil fuels for energy led to mechanized farming, railroads changed the way people traveled and transported raw materials and goods, the demand for labor saw one of the largest migrations in world history to America, and laissez-faire economics provided opportunities for wealth while increasing the divide between the poor and rich. During this period local governments were challenged to meet the needs of large populations in urban areas regarding their health, safety, and education.
Activity #1: The Granger Movement in America (1875) and the Yellow Vests in France (2019)

The Patrons of Husbandry, or the Grange, was founded in 1867 to advance methods of agriculture, as well as to promote the social and economic needs of farmers in the United States. The financial crisis of 1873, along with falling crop prices, increases in railroad fees to ship crops, and Congress’s reduction of paper money in favor of gold and silver devastated farmers’ livelihoods and caused a surge in Grange membership in the mid-1870s. Both at the state and national level, Grangers gave their support to reform-minded groups such as the Greenback Party, the Populist Party, and, eventually, the Progressives.
The social turmoil that the Western farmers were in was mainly a result of the complete dependence on outside markets for the selling of their produce. This meant that they had to rely on corporately owned railroads and grain elevators for the transport of their crops. To make matters worse, “elevators, often themselves owned by railroads, charged high prices for their services, weighed and graded grain without supervision, and used their influence with the railroads to ensure that cars were not available to farmers who sought to evade elevator service.” In 1871, Illinois created a new constitution allowing the state to set maximum freight rates but the railroads simply refused to follow the mandates of the state government.
The Grangers became political by encouraging friends to elect only those officials with the same views. Furthermore, while Republicans and Democrats had already been bought out by corporations looking to curry favor in the government, Grangers vowed to create their own independent party devoted to upholding the rights of the general populace.
On Independence Day, 1873 (known as the Farmer’s Fourth of July), the Grangers read their Farmer’s Declaration of Independence, which cited all of their grievances and in which they vowed to free themselves from the tyranny of monopoly. The Supreme Court decision in Munn v. Illinois stated that businesses of a public nature could, in accordance with the federal constitution, be subject to state regulation. Following this ruling, several pieces of legislation, collectively known as the Granger Laws, were passed. Unfortunately, many of these laws were repealed.
Though the organization did not last, it demonstrated the effects that monopolies have on society. It subjugated these individuals to its whims, and then forced them to take action against it.
The Yellow Vests Protest in France

Donning the now-famous fluorescent waistcoats that are mandatory in French cars, the Yellow Vests staged 52 consecutive weeks of protests against economic hardship, mounting inequality and a discredited political establishment. They manned roundabouts across the country night and day, took to the streets on every Saturday since November 17, and at their peak in December even stormed the Arc de Triomphe in central Paris, amid scenes of chaos not witnessed since May ’68. The movement had an indelible mark on France, forcing the government into billions of euros of tax breaks.
“The picture that emerged was that of a movement made up largely of workers and former workers in a situation of financial insecurity, with relatively few unemployed,” said Gonthier. Yellow Vests were present across France, but strongest in small towns and rural areas. They came from all walks of life, but liberal professions were underrepresented, while small business owners and employees, craftspeople and care workers formed the bulk of the movement. About two thirds of respondents earned less than the average wage, and a slightly higher percentage registered as having a “deficit of cultural resources and social links”. This in turn “conditioned the way they defined themselves, and helped distance them from traditional social movements”, Gonthier added.
Another defining feature was the high proportion of women, who made up roughly half the Yellow Vests, whereas social movements traditionally tend to be male-dominated. Gonthier said this reflected the significant mobilization of women in care work, “most notably hospital workers from a public health sector that is plunging deeper into crisis”. They included a high number of single mothers who couldn’t go out and protest, or were scared away by the police’s heavy-handed response, but who supported the movement online.
Questions:
- Are monopolies harmful to a growing economy or are they a necessary ‘evil’?
- Is it inevitable that an oppressed people will revolt and attempt to destroy that which has kept them down?
- How can governments best address poverty and inequality?
- If a significant minority feels oppressed, do they have a right to overthrow their government by protest or violence if they cannot get satisfaction through the process of elections?
- Do you support the Grangers, Yellow Vests, both or neither?
A Brief Essay on the Grange Movement
Who are France’s Yellow Vest Protestors and What do they Want?
The Yellow Vest Movement Explained
Activity #2: Munn-Wabash Railroad in Illinois and the Trans-Siberian Railroad in Russia
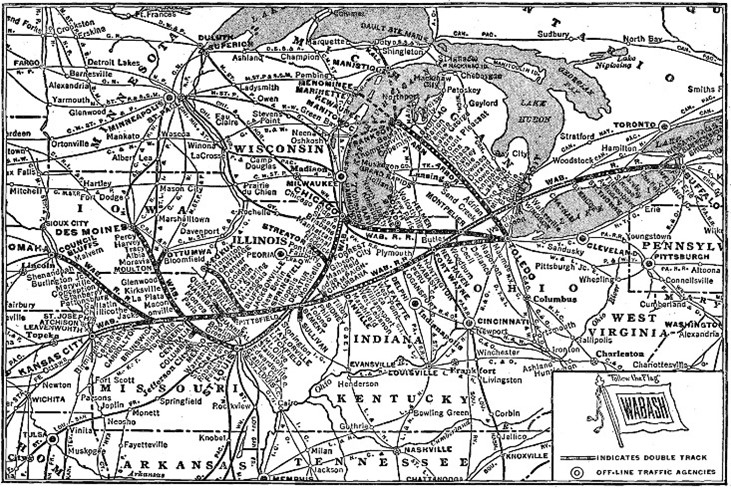
Route of the Wabash Railroad in the Midwest
The Wabash Railroad Company went bankrupt and was sold. The new Toledo and Wabash Railroad Company was chartered October 7, 1858. The Wabash and Western Railroad was chartered on September 27 and acquired the Indiana portion on October 5. On December 15, the two companies merged as the Toledo and Wabash Railway, which merged with the Great Western Railway of Illinois. The right of continuous transportation from one end of the country to the other is essential in modern times to that freedom of commerce. The Commerce Clause in the U.S. Constitution gives Congress the power to regulate commerce among the States and with foreign nations. If Illinois or any other state within whose were permitted to impose regulations concerning the price, compensation, or taxation, or any other restrictive regulation it would be harmful to commerce between states.
The Trans-Siberian Road in Russia

Trans-Siberian Railroad Crossing a large river in Siberia
The construction of the longest railway in the world was launched in April 1891 and was completed in 1894. Three years later the section between Vladivostok to Khabarovsk with a length of 772km was opened in November 1897. The Central Siberian Railway from the River Ob to Irkutsk with a length of 1839km was built in 1899. The construction involved more than 100,000 workers, including prisoners, and the work was carried out by hand using shovels, axes, crowbars, saws. Despite the many challenges of the taiga, mountains, wide rivers, deep lakes, and floods, the tracks were built with amazing speed – around 740km per year.
Questions:
- Does the protection of technology for the efficiency of commerce justify federal regulations over state regulations?
- If a corporation is losing money, do they have a right or obligation to raise rates to become profitable?
- Do authoritarian governments have an advantage or disadvantage in the construction of large infrastructure projects?
Consolidation of Railroads in Four States
The Supreme Court Strikes Down Railroad Regulation
Interstate Commerce Act (1887)
Construction of the Trans-Siberian Railroad
History of the Trans-Siberian Road
Activity #3: The Debt Crisis of the U.S. Government in 1894 and Inflation in Weimar Germany in 1923.

No crisis of the Cleveland presidencies exceeded the magnitude of the financial panic that gripped the nation at the start of his second term in 1893, and which presaged a depression that still lingered when he left office in March 1897.
The Constitution granted Congress the power “to coin money, regulate the value thereof, and of foreign coin, and fix the standard of weights and measures.” (Article 1, Section 8) Article I, Section 8, and Clause 2 The Congress shall have power to borrow money on the credit of the United States. In the 14th Amendment, Section 4, it states that “the validity of the public debt of the United States, authorized by law … shall not be questioned.”
In the century preceding 1893, Congress experimented with two central banks, a national banking system, laws regulating so-called “wildcat banks,” paper money issues, legalized suspension of specie payments, and fixed ratios of gold and silver. Gold and silver rose to prominence as the predominant monies of the civilized world because of their scarcity and value. Under the direction of Alexander Hamilton, the federal government adopted an official policy of bimetallism and a fixed ratio of 15 to 1 in 1792.
In 1875, the newly-formed National Greenback Party called for currency inflation through the issuance of paper money tied, at best, only minimally to the stock of specie. The proposal attracted widespread support in the West and South where many farmers and debtors joined associations to lobby for inflation, knowing that a reduction in the value of the currency unit would alleviate the burden of their debts.
When President Cleveland assumed office on March 4, 1893, the Treasury’s gold reserve stood at the historic low of $100,982,410 — slightly above the $100 million minimum required for protecting the supply of greenbacks. The Panic of 1893 began when the gold reserves fell below $100,000,000. Stocks fell and factories closed with many going bankrupt. Unemployment rose to 9.6%, nearly three times the rate for 1892. By 1894, the unemployment rate was almost 17%. The Sherman Silver Purchase Act was repealed in support of gold as a stable currency.
Cleveland’s position on sound money was not supported by his Democratic Party. The Gold Standard Act of 1900 resulted in a stable gold standard and economic growth. Cleveland’s position on sound money worked.
Hyperinflation in Germany

Under the Treaty of Versailles Germany was forced to make a reparations payment in gold-backed Marks. On June 24, 1922, Walter Rathenau, the foreign minister was assassinated. The French sent their army into the Ruhr to enforce their demands for reparations and the Germans were powerless to resist. More than inflation, the Germans feared unemployment. A cheaper Mark, they reasoned, would make German goods cheap and easy to export, and they needed the export earnings to buy raw materials abroad. Inflation kept everyone working.
The price increases began to be dizzying. Menus in cafes could not be revised quickly enough. For example, a student at Freiburg University ordered a cup of coffee at a café for 5,000 Marks. He had two cups but when the bill came, it was for 14,000 Marks. When the 1,000-billion Mark note came out, few bothered to collect the change when they spent it. By November 1923, with one dollar equal to one trillion Marks, the breakdown was complete. The currency had lost meaning and value.
Although the currency was worthless, Germany was still a rich country — with mines, farms, factories, forests. The backing for the new Rentenmark was the value of the land for mortgages and bonds for the factories. Since the factories and land couldn’t be turned into cash or used abroad the value of one Rentenmark was equal to one billion of the former Marks. People lost their savings and homes.
Questions:
- Is a sound currency policy, where the dollar is backed by gold or some other form of credit, always the best policy for governments to follow?
2. Does the financial debt of a country matter if its economy is growing? Does it matter in times of war or the recovery from a natural disaster?
3. In a financial crisis, a depression, does everyone suffer equally or are some more affected than others?
4. Which problem should the government address first? High Unemployment of 8% or rising inflation of 5%? Why?
5. Is foreign investment in a country’s economy necessary to maintain a balance of payments?
6. Based on the U.S. Constitution, is the debt of our government limited or unlimited?
The Panic of 1893 and the Election of 1896
The German Hyperinflation, 1923
Activity #4: The debate over Laissez-faire Economics
Historians often call the period between 1870 and the early 1900s the Gilded Age. This was an era of rapid industrialization, laissez-faire capitalism, and no income tax. Captains of industry like John D. Rockefeller and Andrew Carnegie made fortunes. They also preached “survival of the fittest” in business.
By the late 1800s, however, monopolies, not competing companies, increasingly controlled the production and prices of goods in many American industries.
Workers’ wages and working conditions were unregulated. Millions of men, women, and children worked long hours for low pay in dangerous factories and mines. There were few work-safety regulations, no worker compensation laws, no company pensions, and no government social security.
Starting in the 1880s, worker strikes and protests increased and became more violent. Social reformers demanded a tax on large incomes and the breakup of monopolies. They looked to state and federal governments to regulate capitalism. They sought legislation on working conditions, wages, and child labor.
Railroad builders accepted grants of land and public subsidies in the 19th century. Industries facing strong competition from abroad have appealed for higher tariffs. American agriculture benefited with land grants and government support. State governments helped finance canals, railroads, and roads.
It is difficult to separate government intervention, regulation, and laissez-faire in American history. It is likely even more difficult to find the proper balance between government and free enterprise. Perhaps the most serious violations occurred during this era in America’s history with land grants to railroads, regulating the rates railroads could charge, mandating time zones, and allowing paper currency.

Questions:
- Why is limited government and laissez-faire economics popular in the United States over time and today?
- Should the federal government regulate education and schools or should this be left to the local and state governments?
- Does laissez-faire economics bridge or widen the income gap between the social classes?
- Who benefits the most from increasing government regulation?
Laissez-faire Economics in Practice