New Jersey Council for the Social Studies
Engaging High School Students in Global Civic Education Lessons in U.S. History
The relationship between the individual and the state is present in every country, society, and civilization. Relevant questions about individual liberty, civic engagement, government authority, equality and justice, and protection are important for every demographic group in the population. In your teaching of World History, consider the examples and questions provided below that should be familiar to students in the history of the United States with application to the experiences of others around the world.
These civic activities are designed to present civics in a global context as civic education happens in every country. The design is flexible regarding using one of the activities, allowing students to explore multiple activities in groups, and as a lesson for a substitute teacher. The lessons are free, although a donation to the New Jersey Council for the Social Studies is greatly appreciated. www.njcss.org
Era 7 The Emergence of Modern America: World War I (1890–1930)
The beginning of the 20th century marks the foundation of the transformation of the United States into a world power by the middle of the century. In this era industrialization, urbanization, and rapid immigration changed America from an agrarian to an urban society as people lived and worked in cities. The development of the new technologies of electricity, transportation, and communication challenged our long-held traditional policies of limited government, neutrality, and laissez-faire capitalism.
Activity #1: The Power ofDollar Diplomacy in the United States (1914) and Qatar (2014)

President Theodore Roosevelt’s foreign policy was popularized with a 20th century interpretation of the Monroe Doctrine. The Roosevelt Corollary (1904) stated that the United States would intervene as a last resort to ensure that other nations in the western Hemisphere fulfilled their obligations to international creditors and did not violate the rights of the United States or invite foreign aggression to the detriment of the entire body of American nations. The expansion of our navy changed the Monroe Doctrine from a passive to an assertive policy that justified the intervention of the United States in Cuba, Haiti, Nicaragua, and the Dominican Republic, as well as an American presence in Panama, China, and the Philippines. When President William Howard Taft became president in 1909, his foreign policy substituted dollars for bullets. He formalized his vision in his 1912 State of the Union Address:
“The diplomacy of the present administration has sought to respond to modern ideas of commercial intercourse. This policy has been characterized as substituting dollars for bullets. It is one that appeals alike to idealistic humanitarian sentiments, to the dictates of sound policy and strategy, and to legitimate commercial aims.”
President Taft focused on trade and he refinanced the debts of several countries in Central America who were at risk of default. He supported private economic investment in China to counter the aggression of Japan and maintain the balance of power in East Asia.
Taft’s policy led to the rise of nationalist movements who opposed the influence or interference of the United States and in China where the investments in infrastructure by Americans and American companies led to mistrust. His successor, President Wilson introduced “Moral Diplomacy” as his vision for diplomatic leadership, which included sending American troops to Haiti, Nicaragua, the Dominican Republic, and Mexico.
Dollar Diplomacy in Qatar
Qatar is a small Persian Gulf state with a population of less than 3 million and one of the highest per capita GDPs in the world at $85,500 USD. It is about half the size of New Jersey and close in size to Connecticut. It is the richest country in the world and most of its wealth comes from natural gas and petroleum.
In 2017 Saudi Arabia, Egypt, the United Arab Emirates, and Bahrain imposed a blockade on Qatar because of their support for the Muslim Brotherhood and Iran. Qatar is currently using its wealth to promote international relations and trade and investment agreements with Russia, Central America, South Africa, Europe, and several U.S. energy companies. Qatar produces Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) which is becoming more popular to offset carbon emissions. In 2021, the blockade ended.
Qatar has hosted the Doha trade talks, the World Cup, pledged $500 million to the United Nations’ programs, and has been central to the negotiations between Israel and Hamas on the release of hostages and humanitarian supplies.
Questions:
- Is there a difference between Dollar Diplomacy and economic imperialism?
- Why did Dollar Diplomacy fail in the Taft Administration and is it likely to meet with failure in Qatar?
- What is the most effective way to change the position of a country that supports terrorist organizations?
- Does the richest country in the world have more power than the country with the strongest military?
- Should the United States become less trustworthy of Qatar or does pragmatism suggest that by increasing our economic agreements we will attain more benefits than disappointments?
- Is it the role and responsibility of the Legislative or Executive Branch to decide foreign policy in the United States?
William Howard Taft’s Dollar Diplomacy
The Qatar Blockade is over but the Gulf Crisis Lives On
Activity #2: Child Labor Laws in the United States and Ivory Coast
From a Civics perspective, the issue of child labor is about the amount of regulation by the federal and state government that is necessary to protect children from exploitation under the Commerce Clause. The United States v. Darby decision by the U.S. Supreme Court (1941) is a landmark case that supports federal regulation of child labor.
Food insecurity is a problem for more than 10% of American families who might benefit from additional income. The historically low unemployment rate of 4% or less in the United States also creates demand for additional workers. National Labor Statistical (NLS) data show that 52% of 12 and 13-year-olds have paid work experience. The work performed at these ages was found to be freelance in nature. Babysitting and yardwork accounted for more than 70 percent of the work they performed. For 14 and 15-year-olds, the dominant form of work is also freelancing. It is estimated that 153,600 children are employed at an activity in violation of the FLSA or state law on a weekly basis. Many are children of migrant families whose labor may be exploited. The most common violations entail working excessive hours or engaging in a hazardous occupation before the age of 18.
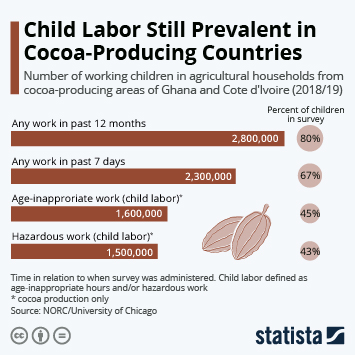
Child Labor in the Ivory Coast
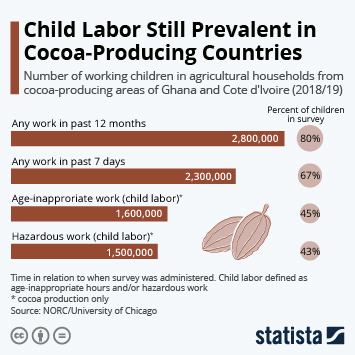
Children in Côte d’Ivoire are subjected to the worst forms of child labor, including in the harvesting of cocoa and coffee, sometimes as a result of human trafficking. Children who work in cocoa production are often deprived of adequate schooling. Children who carry heavy loads of cocoa are exposed to pesticides, insect and snake bites, machete wounds, fatigue and leg and back problems.
In 2016, in light of the Harkin-Engel Agreement, the National Plan for fighting Against Child Labor and Child Trafficking, numerous Government, NGO and private sector initiatives and projects were being implemented in Cote d’Ivoire to improve productivity, community development and child rights in cocoa producing areas.
Questions:
- Should states be allowed to make their own laws about child labor laws when work is being done only withing their state?
- Should parents be empowered to make the decisions regarding employment for their children under age 16 or another age?
- Do you agree with the federal District Court or the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision on Darby?
- Should volunteer work under the supervision of a nonprofit organization be exempt from child labor law requirements? (soccer referee v. construction of affordable houses)
- Should there be a requirement by the government for employers to monitor and report child employment?
History of Child Labor in the United States
Child Labor Laws are Under Attack in the United States
Child Labor in the Côte d’lvoire
U.S. State Department Report on Trafficking in Cote d’Ivore in 2022
Activity #3: The Power of Government to Control Private Enterprises in the United States and India
The Framework for Private Enterprise in the United States
The government of the United States regulates businesses by taxing them. There are income taxes, employment taxes, excise taxes, and local and state taxes. The government also offers tax incentives for businesses to locate in areas of poverty and to hire veterans, women, minorities, and individuals with disabilities. The federal and state governments also regulate price increases for public utilities, credit and have laws to prevent monopolies or price-fixing. Health and safety regulations are regulated to protect workers from injury, toxic substances, excessive noise, and a safe and clean environment. There are also regulations on equal pay for jobs with the same or similar skills and the hours worked. The government requires retirement programs for larger businesses and has laws to protect consumers.
The Framework for Private Enterprise in India
In India, it is in the interest of the government and private sector to improve the productive capacity of the country and its citizens. This improvement leads to real wage growth, more competition and increased consumption.
The top 5 companies in India have a total market value of 20% of India’s GDP. The government needs these industries to create jobs.
Chips were originally developed for the American government and then were licensed out to benefit consumer technology products, Mobile networks were originally built for the defense need in America and Finland, and GPS was broad based by President Clinton after Russia shot down a Korean 747 for straying into their airspace.
India needs to further strengthen the governance of state-owned enterprises, simplify regulations, and reduce administrative burdens on firms. India should also review its institutions responsible for regulation and compliance.
Questions:
- Should the primary focus of government regulation emphasize the protection of workers and consumers or to increase innovation and economic growth?
- Does the cost of regulation through the payment of taxes limit economic growth or is it necessary to develop a balanced economy?
- Investigate areas in public education that are regulated by the local, state, or federal government and identify which regulations are helpful and which are harmful to students and teachers?
Examples of Government Regulation of Business in the United States
Where does the Public Sector End and the Private Sector Begin?
Activity #4: The Roosevelt Corollary in the Caribbean and China’s Hegemony in the South Pacific
The Roosevelt Corollary (1904)
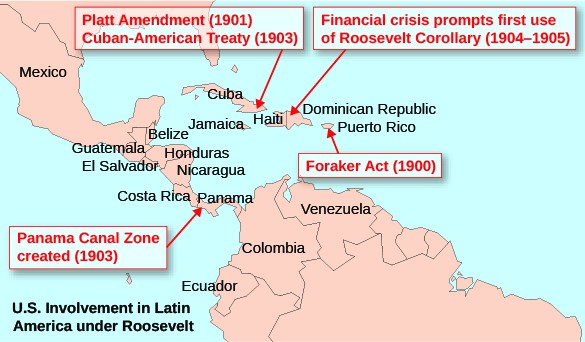
The Roosevelt Corollary of December 1904 stated that the United States would intervene as a last resort to ensure that other nations in the Western Hemisphere fulfilled their obligations to international creditors. The United States was concerned that other nations might take advantage of the default on debts by some countries in the Caribbean. The United States considered the islands in the Caribbean to be of strategic commercial and military importance. President Roosevelt’s position justified U.S. intervention in Cuba, Nicaragua, Haiti, and the Dominican Republic.
The United States is concerned about the increased economic investment by China in several countries in the South Pacific and the diplomatic changes by these island countries ending their support for Taiwan and agreements with China.
China’s Presence in the South Pacific (2024)
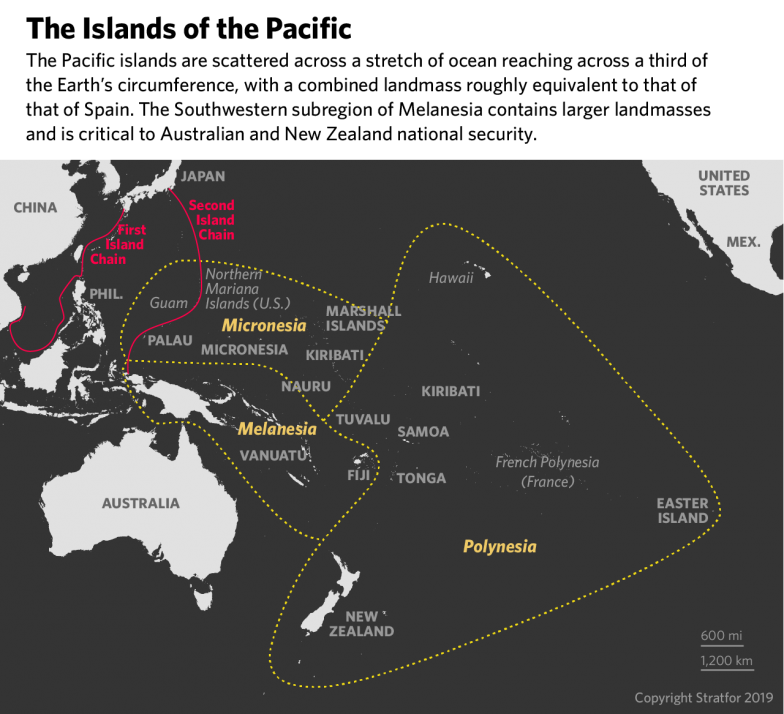
Since World War II the Pacific has largely enjoyed independence from foreign influence. There are 14 independent island countries in this area and although they are at risk of rising sea levels and natural disasters, they also have strategic military importance. This has all changed with China’s growing presence in the region.
Australia is an ally of the United States through the Southeast Asia Treaty Organization (SEATO). A military base by China would present a serious threat to its security. However, China’s interests may also be economic. China is investing in infrastructure projects in the South Pacific with investments on an equal level with Australia and the United States.
In 2022, China entered into a security agreement with the Solomon Islands. This agreement provides China with an operational military base about 2,000 miles from Australia. There is no definitive understanding of why China is increasing its presence in this region and the risks may be minimal. The importance for a conversation about civics is about the right of a major global power to enter into secret or public diplomatic, military, or commercial agreements with other nations. For the United States, should our foreign policy regarding South Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Guam, and Australia be determined by the Executive or Legislative Branch in our government?
China needs to consider the economic cost of its investments in these small islands that are in debt as the impact of rising sea levels is likely to limit their economy and increase their debt. Will the economic costs weaken instead of strengthening China in the future?
Australia also needs to re-evaluate its objectives for security as naval and air support from the United States and other countries may be limited by China’s presence in this area. The distance from the United States to Japan, Taiwan, and Australia is much further than it is for its rivals of North Korea, Russia, and China.
Questions:
- Do countries have the right to extend their economic, military, or diplomatic influence to advance their own security or objectives? (Israel, Russia, China, Iran, United States, etc.)
- How should the United States determine its foreign policy when Congress and the President cannot agree?
- How important is geography in developing a country’s foreign policy?
- Does an authoritarian government have an advantage or disadvantage in developing its foreign policy?
- Do the foreign policies and laws for countries change as the 21st century military utilizes artificial intelligence and space?
President Theodore Roosevelt’s State of the Union Address: The Roosevelt Corollary (1904)
The Roosevelt Corollary (1904)
The Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine
